AXIS BANK Limited – Badhti Ka Naam Zindagi.
Date Published: November 18, 2022

Company Overview
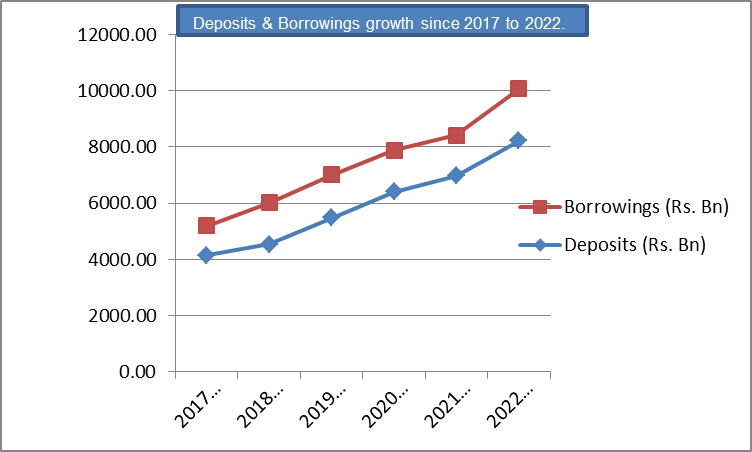
Axis Bank is the third largest private sector bank in India. The Bank offers the entire spectrum of financial services to customer segments covering Large and Mid-Corporates, MSME, Agriculture and Retail Businesses. The Bank has a large footprint of 4,758 domestic branches (including extension counters) with 10,990 atms & 5,972 cash recyclers spread across the country as of 31st March 2022. The Bank has 6 Axis Virtual Centers with over 1,500 Virtual Relationship Managers as of 31st March 2022. The Overseas operations of the Bank are spread over eight international offices with branches in Singapore, Dubai (at DIFC), and Gift City-IBU; representative offices in Dhaka, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah and an overseas subsidiary in London, UK. The international offices focus on Corporate Lending, Trade Finance, Syndication, Investment Banking, Liability Businesses, and Private Banking/Wealth Management offerings. Axis Bank is one of the first new generation private sector banks to have begun operations in 1994. The Bank was promoted in 1993, jointly by Specified Undertaking of Unit Trust of India (SUUTI) (then known as Unit Trust of India), Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC), National Insurance Company Ltd., The New India Assurance Company Ltd., The Oriental Insurance Company Ltd., and United India Insurance Company Ltd. The shareholding of Unit Trust of India was subsequently transferred to SUUTI, an entity established in 2003. With a balance sheet size of Rs. 11,75,178 crores as on 31st March 2022, Axis Bank has achieved consistent growth and with a 5-year CAGR (2016-17 to 2021-22) of 14% each in Total Assets & Advances and 15% in Deposits.
Industry Overview
India’s Banking Sector is composed of public sector Banks and private sector banks, foreign banks and small finance banks along with Co-operative banks(urban and rural) and non-banking financial institutions(NBFIs). The sector is regulated and governed by the RBI, which was established in April 1935 in accordance with the provision of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The government allowed the entry of private players in the countrys banking sector in the 1990s. Lately, the banking sector has been withnessing increased competition, the launch in go finnovative products, and enhanced adoption of digitization, which also brought Indias fintech land scape to prominence. According to the Indian ICRA rating agency, Outlook for Indian Banking sector has shifted from “Stable” to “improving” for FY2023, let by better credit demand and the strong balance sheet for lenders. With strengthened balance sheets and an improved credit demand outlook, the key financial metrics are likely to continue to show improvement in FY 2023, with an expected initiation of the corporate capex cycle. Another thing which is to improve in the coming year and onwards, is the quality of the mobile banking apps of lenders.
Axis Bank starts digital lending through Account Aggregator Framework
Axis Bank has been an early investor in the Account Aggregator ecosystem, which has helped the Bank to build the tech stack to operationalize its AA framework and offer a seamless customer-friendly experience. The bank offers personal loans, credit cards, auto loans and small business loans through the account aggregator journey. It provides instant loans that are completely digital and paperless, both for existing and new customers. Axis Bank is already live on multiple Account Aggregators like Anumati-AA, OneMoney-AA, FinViu–AA, covering retail and SME customers. The Bank’s loan disbursals have increased more than 30% month-on-month since Go–Live on the Account Aggregator framework. Account Aggregator framework is a powerful proposition which is scaling up rapidly. It provides easy and instant access to financial information of customers in a safe and secure manner. Being able to access this data securely enables the banks to build new customer friendly journeys in Lending, Credit Monitoring and Wealth Management. The information comes from a trusted source and is completely digital, leading to customer delight and operational efficiencies.
Company Growth parameter:
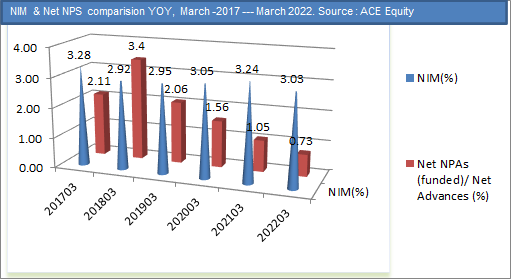
Asset quality improves with further moderation of Slippages:
The fresh slippages for Q1FY23 were at INR 36,840 Mn, down by 7.5% QoQ/ 43.5% YoY. The gross loan slippage ratio for the quarter stood at 2.05%, declining by 210 bps YoY and 33 bps QoQ. In Q1FY23, 45.0% of the gross slippages are attributed to borrowers’ linked accounts, which were standard when classified or upgraded in the same quarter. The recoveries and upgrades for Q1FY23 were at 29,570 Mn. The GNPA and NNPA ratios of the bank have improved at 2.76% and 0.64%, respectively, as against 2.82% and 0.73% as of March 31, 2022. The bank’s PCR stood at 77% for the quarter. The BB and Below pool of the bank continued to decline by 38.0% YoY and 13.0% sequentially. We expect asset quality to remain stable, with a gradual decline in slippages going ahead.
Credit growth led by retail; unsecured growth higher:
Total loans increased by 14% YoY, but declined by ~1% QoQ mainly on account of decline in corporate and SME loans. Growth (YoY) was led by retail (+25% YoY) and CBG (+27% YoY). Corporate loans declined by 5% YoY and 6% QoQ as the bank chose not to pursue low-yielding corporate assets amid thin margins and instead focused on profitable/margin-accretive growth. In the retail portfolio, mortgages continued to see strong growth trends, in line with other large peers. Home Loan portfolio increased by 18% YoY (1% QoQ) while the LAP portfolio grew by 26% YoY (2% QoQ). Unsecured retail loans (PL + CC) also saw strong growth, in line with peers, aided by strong demand and banks’ comfort post-covid. The share of secured disbursements in overall disbursements declined to 78% in 1QFY23 from 82% in 4QFY22 and 79% in 1QFY22. PL portfolio increased by 20% YoY and 4% QoQ while credit card loans increased by 42% YoY and 14% QoQ. Auto and rural loans increased by 14% YoY and 42% YoY, respectively. In the overall wholesale segment, the growth trends across sub-categories are reflective of the management’s strategy to scale up the mid-corporate segment. Mid-corporate loan book increased by 54% YoY and 5% QoQ. Over the longer term, the retail portfolio is expected to grow at a higher rate. Given the QoQ drop in loans, we have cut our loan growth estimates. The Citi acquisition is expected to be completed by 4QFY23-end.
Valuation and Outlook:
Axis bank is confident that with rates increasing, pricing stabilizing and corporate demand reviving, it is well positioned to chase growth in the corporate segment. The bank is guiding for 3.7-3.8% NIM in the next 8-10 quarters, driven by improving loan mix and overall balance sheet mix. Cost ratios remained elevated at 2.2-2.3% on account of investments in technology and growth areas. Asset quality improved, a trend in line with the overall banking industry trend. Despite all the stress indicators showing sequential improvement, the bank has topped up its PCR by 200-250bps. Overall credit cost is expected to remain <1%. We have cut our earnings by 0.6-2.2% over FY23-24E and expect the bank to report 1.2- 1.4% ROE. Valuation comfort underpins our BUY stance on Axis Bank despite lower ROA than HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank. We maintain BUY with a target price (TP) of Rs850 considering a forward EPS of 54.12 and 71.1 for FY 2023/2024 as compared to EPS of 52.4 for FY 2022.